AMD is preparing to expand its ambitious Strix Halo processor lineup with two new variants that promise to deliver gaming-capable integrated graphics performance at more accessible price points. The Ryzen AI Max+ 388 and Ryzen AI Max+ 392 were recently spotted in benchmark databases and later confirmed by Chinese PC manufacturer SixUnited.
The Strategic Gap in the Lineup
When AMD launched its Strix Halo platform in January 2025, the lineup consisted of three main processors: the flagship 16-core Ryzen AI Max+ 395 with 40-compute-unit Radeon 8060S graphics, and two lower-tier models – the 12-core Ryzen AI Max 390 and 8-core Ryzen AI Max 385 – both featuring the cut-down 32-compute-unit Radeon 8050S graphics.
This configuration created an interesting dilemma for potential buyers. If you wanted the full graphical capabilities of the Radeon 8060S, you had just one option: the expensive 16-core flagship model, which commands premium pricing typically reserved for high-end laptops priced at $2,000 and above. For gamers looking for an affordable gaming laptop with decent GPU capabilities, this is obviously not an option.
The newly revealed Ryzen AI Max+ 388 and 392 address this gap directly. According to information from VideoCardz, both new CPUs retain the full 40-compute-unit Radeon 8060S integrated graphics while reducing CPU core counts and cache sizes.
- The Ryzen AI Max+ 388 features 8 cores and 16 threads with boost clocks reaching 5.0 GHz, alongside 32MB of L3 cache and 8MB of L2 cache. This configuration mirrors the core count of the entry-level Ryzen AI Max 385 but pairs it with the flagship’s powerful integrated GPU.
- The Ryzen AI Max+ 392 occupies the middle ground with 12 cores and 24 threads, also boosting to 5.0 GHz. It includes 76MB of total cache, matching the Ryzen AI Max 390’s configuration while maintaining the full Radeon 8060S graphics capability.
The “Max+” designation in AMD’s nomenclature appears to denote processors equipped with the full 40-compute-unit Radeon 8060S graphics, differentiating them from standard “Max” models that feature the reduced 32-compute-unit configuration.
Performance Expectations
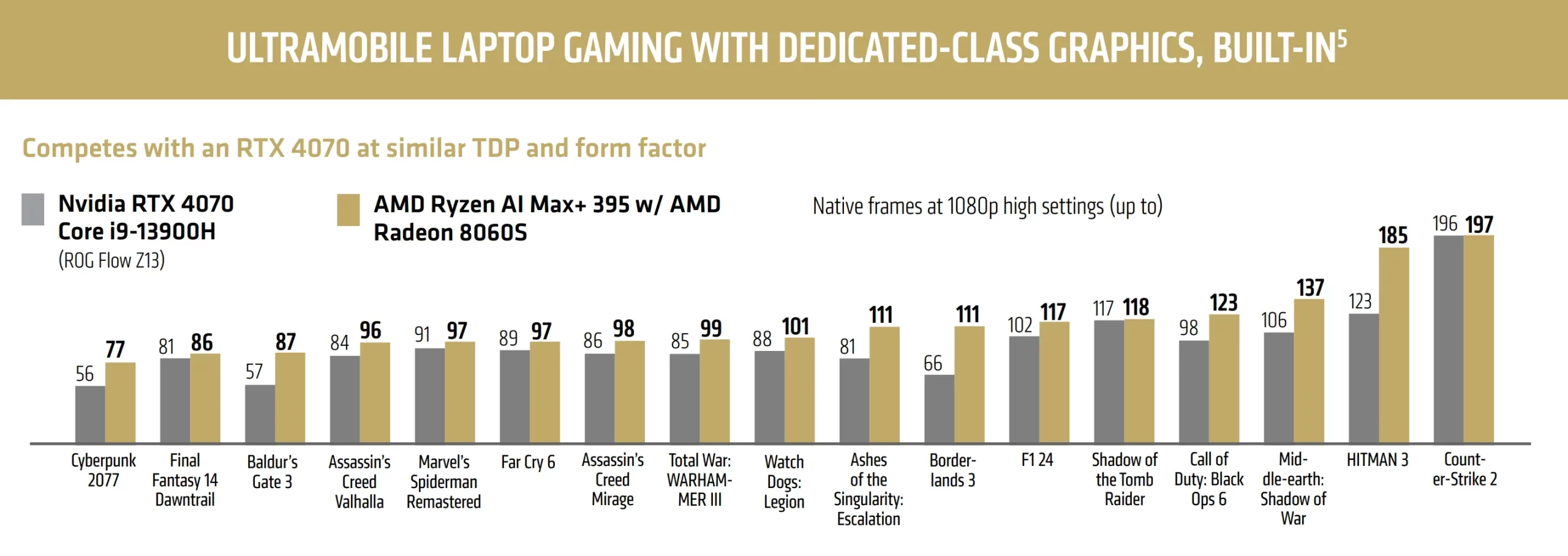
The Radeon 8060S has established itself as a genuinely capable gaming solution. AMD’s own testing demonstrates that the integrated GPU can compete with discrete graphics cards like the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Laptop GPU in 1080p gaming scenarios, with AMD claiming up to 68% better performance in titles like Borderlands 3 and an average 23% advantage across 17 tested games.
In-house benchmarks are often cherry-picked, but reviews from Phoronix and others confirm that Strix Halo’s integrated graphics deliver performance somewhere between an RTX 4060 and RTX 4070 in laptop form factors. For 1080p gaming at high settings, most modern titles achieve playable frame rates of 60 FPS or higher without requiring a discrete GPU.
The reduced CPU core counts in the new variants should have minimal impact on gaming performance. Modern games rarely scale beyond 8-12 threads effectively, meaning the 8-core Max+ 388 will likely deliver nearly identical gaming performance to the 16-core Max+ 395 in most scenarios.
Other than gaming, Strix Halo processors also excel at AI workloads thanks to their combination of high memory bandwidth and substantial unified memory capacity. All Strix Halo variants include AMD’s XDNA 2 Neural Processing Unit rated at 50 TOPS, but the real AI performance advantage comes from the ability to allocate up to 96GB of system memory as VRAM when equipped with 128GB of LPDDR5X RAM (a scenario that will never apply to mainstream laptops).
Market Positioning and Competition
The Strix Halo platform operates in a unique segment of the mobile processor market. Unlike AMD’s mainstream Strix Point processors, which compete directly with Intel’s Lunar Lake chips in thin-and-light laptops, Strix Halo targets a different audience: users who need workstation-class integrated graphics without the bulk and cost of a discrete GPU.
Intel’s closest competitor is theoretically the upcoming Panther Lake processors, which feature improved Xe3 graphics cores. Early benchmarks suggest Panther Lake’s flagship Core Ultra X9 388H achieves up to 50% better graphics performance than Lunar Lake, scoring around 6,300 points in 3DMark TimeSpy. However, this still falls well short of Strix Halo’s capabilities, as the Radeon 8060S operates at a much higher power envelope – up to 120W versus Panther Lake’s 45W target TDP.
Technical Specifications
| Model | CPU Cores / Threads | Base / Boost Clock | Total Cache | Integrated Graphics | GPU Compute Units | TDP Range | NPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen AI Max+ 395 | 16 / 32 | 3.0 / 5.1 GHz | 80 MB | Radeon 8060S | 40 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W | 50 TOPS |
| Ryzen AI Max+ 392* | 12 / 24 | TBD / 5.0 GHz | 76 MB | Radeon 8060S | 40 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W (est.) | 50 TOPS |
| Ryzen AI Max 390 | 12 / 24 | 3.2 / 5.0 GHz | 76 MB | Radeon 8050S | 32 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W | 50 TOPS |
| Ryzen AI Max+ 388* | 8 / 16 | TBD / 5.0 GHz | 40 MB | Radeon 8060S | 40 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W (est.) | 50 TOPS |
| Ryzen AI Max 385 | 8 / 16 | 3.6 / 5.0 GHz | 40 MB | Radeon 8050S | 32 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W | 50 TOPS |
| Ryzen AI Max Pro 380 | 8 / 16 | 3.7 / 5.0 GHz | 40 MB | Radeon 8050S | 32 CU (RDNA 3.5) | 45-120W | 50 TOPS |
* Unannounced models based on leaked specifications. All Strix Halo processors use Zen 5 architecture on 4nm process, support LPDDR5X-8000 memory with 256GB/s bandwidth, PCIe 4.0, and USB4.
AMD has not officially announced the Ryzen AI Max+ 388 or 392 processors, and specific pricing information remains unavailable. However, the chips’ appearance in benchmark databases and confirmation by system integrators suggests a launch may be imminent, potentially at CES 2026 or another major industry event.
Current Strix Halo systems typically start around $2,000 for configurations with the flagship Ryzen AI Max+ 395, with high-end models like HP’s ZBook Ultra workstations reaching $3,000 or more. The introduction of 8-core and 12-core variants with full graphics capability should enable manufacturers to offer systems at more reasonable prices.





